Calculate Your Body Mass Index (BMI)
Your BMI
BMI is a screening tool, not a direct measure of body fat or health.
Check Your Obesity Risk Level
Obesity Risk Assessment
Your BMI: -
BMI Risk
-
Waist Risk
-
Lifestyle Factors
-
Recommendations
-
RELATED TOOLS
HOME
OTHERS
TRY MORE CALCULATORS
How to Use the Obesity Risk Calculator
This obesity risk calculator helps assess your risk level based on body measurements, lifestyle factors, and family history. Follow these steps:
- Enter Your Age: Input your age in years
- Select Gender: Choose male or female for accurate risk assessment
- Enter Weight: Provide your current body weight in kilograms
- Enter Height: Input your height in centimeters
- Measure Waist Circumference: Enter your waist size to assess abdominal fat risk
- Select Activity Level: Choose how physically active you are
- Indicate Family History: Check the box if obesity or diabetes runs in your family
- Check Obesity Risk: Click the “Check Obesity Risk” button
- View Risk Score: See your overall obesity risk level
- Review BMI Category: Check your BMI and weight classification
- Analyze Risk Factors: Review BMI, waist, and lifestyle-related risks
- Read Recommendations: Get personalized health and lifestyle suggestions
BMI Chart Explained
Understanding your BMI chart can feel confusing at first glance. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about reading and interpreting BMI charts, what your numbers really mean, and how to use this information for better health decisions.
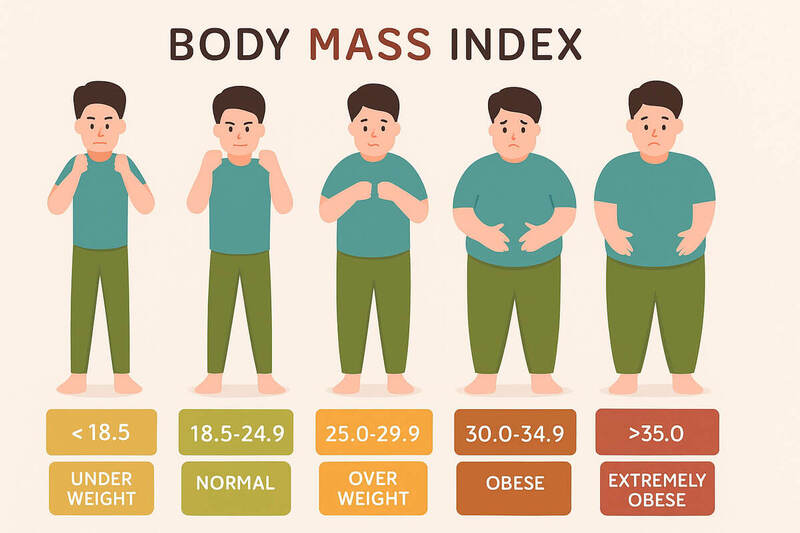
BMI Categories Explained
| BMI Range | Category |
|---|---|
| Below 18.5 | Underweight |
| 18.5 – 24.9 | Healthy Weight |
| 25 – 29.9 | Overweight |
| 30 – 34.9 | Obese (Class I) |
| 35 – 39.9 | Obese (Class II) |
| ≥ 40 | Obese (Class III / Morbid) |
BMI Formulas Explained
BMI Calculation Examples
Example 1: Metric System
Person Details:
- Weight: 70 kg
- Height: 175 cm (1.75 m)
Calculation:
- BMI = 70 ÷ (1.75)²
- BMI = 70 ÷ 3.0625
- BMI = 22.9
Category: Normal weight
Interpretation: Healthy weight range
Example 2: Imperial System
Person Details:
- Weight: 180 lbs
- Height: 5 feet 9 inches (69 inches)
Calculation:
- BMI = (180 ÷ 69²) × 703
- BMI = (180 ÷ 4,761) × 703
- BMI = 0.0378 × 703
- BMI = 26.6
Category: Overweight
Interpretation: Above healthy weight range; consider weight management
Healthy(Normal) Range Of BMI
The healthy normal range of bmi for men, women and kids lies from 18.9 to 24.9
BMI vs Obesity Risk
Bmi and Obesity have close relation:
Example Jhon BMI showed “Normal weight.” But he had belly fat, low activity, and family history of diabetes. Our obesity risk checker showed moderate risk, helping him understand why BMI alone wasn’t enough.
Alisa BMI was “Overweight,” but her obesity risk was low due to active lifestyle and diet. BMI scared her risk checker clarified reality.
What To Do With My BMI Result
Underweight (BMI below 18.5)
You may be undernourished or not getting enough calories, protein, or essential nutrients. Eat nutrient-rich, high-calorie foods like nuts, avocados, eggs, milk, and whole grains. Add healthy snacks between meals. Focus on strength-building exercises to increase muscle mass.
Normal Weight (BMI 18.5 – 24.9)
Your weight is in a healthy range for your height. Maintain a balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, proteins, and whole grains. Exercise at least 30 minutes daily (walking, jogging, yoga, etc.).
Overweight (BMI 25 – 29.9)
You may be carrying extra body fat that can increase your risk for heart disease, diabetes, and other conditions. Focus on portion control and reduce processed or sugary foods. Exercise regularly — aim for at least 150 minutes of physical activity per week. Drink plenty of water and get enough sleep.
Healthy Ways To Improve BMI And Decrease Obesity Risk
Eat Balanced Diet
Include a mix of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. Avoid skipping meals and try to eat at regular times to maintain energy and metabolism.
Stay Hydrated
Drink at least 6–8 glasses of water daily. Staying hydrated helps control appetite, improves digestion, and supports fat metabolism.
Exercise Regularly
Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate physical activity per week — like walking, cycling, or swimming. Add some strength training to build lean muscle, which helps burn calories even at rest.
Get Enough Sleep
Poor sleep can disrupt hormones that control hunger and weight. Aim for 7–8 hours of quality sleep every night to help maintain a healthy BMI.
Manage Stress
Stress can lead to overeating or unhealthy habits. Try meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to keep your mind and body balanced.
Seek Professional Advice
If your BMI is too low or too high, consult a doctor or dietitian for personalized guidance. They can help you create a healthy plan based on your body type, age, and activity level.
BMI Obesity vs Health
A study published by Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) in 2005 showed that overweight people had a death rate similar to normal weight people as defined by BMI, while underweight and obese people had a higher death rate.
A study published by The Lancet in 2009 involving 900,000 adults showed that overweight and underweight people both had a mortality rate higher than normal weight people as defined by BMI. The optimal BMI was found to be in the range of 22.5–25. The average BMI of athletes is 22.4 for women and 23.6 for men.
High BMI is associated with type 2 diabetes only in people with high serum gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase.
Diseases With Overweight Or Obesity
artery disease
Obesity
Dyslipidemia
Type 2 diabetes
Gallbladder disease
Hypertension
Osteoarthritis
Sleep apnea
Stroke
Infertility
At least 10 cancers, including endometrial, breast, and colon cancer
Epidural lipomatosis
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a healthy BMI for adults?
A healthy BMI for adults falls between 18.5 and 24.9.
Is obesity worse than overweight?
It might be yes because obesity causes many other health related dieases like type 2 diabetes.
Does stress cause obesity?
Yes, stress can significantly contribute to obesity through both biological and behavioral pathways.
Is a BMI of 27 healthy or overweight?
Yes it comes in overweight.The healthy bmi fall 18.5 to 24.9
Is BMI different for men and women?
The BMI calculation formula is the same for both genders, but interpretation may differ slightly. Women naturally have more body fat than men, and the same BMI may represent different body fat percentages. Some health organizations use gender-specific BMI interpretations.
What's the difference between BMI and body fat percentage?
BMI estimates body fat based on height and weight. Body fat percentage directly measures the proportion of fat vs. lean tissue in your body using specialized equipment. Body fat percentage is more accurate but requires specialized testing.
Does age affect BMI?
The standard BMI categories apply to adults 20-65. Older adults (65+) may have slightly different healthy ranges, with some studies suggesting a BMI of 25-27 may be optimal for longevity. Children and teens use age and gender-specific BMI percentiles, not adult categories.
Can obesity causes diabetes?
Yes, Obesity is a major cause of type 2 diabetes.
Is obesity genetic?
Yes, Obesity has a strong genetic link with studies suggestion genes account for 40% to 70%of the variation in body weight.
How can I improve my BMI?
Regular exercise, balanced diet, and portion control can help you reach a healthier BMI range.
How to prevent obesity?
To prevent obesity focus on balance diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grain while limiting sugar, drinks and unhealthy foods.
What if I'm very muscular?
BMI may incorrectly classify muscular individuals as overweight or obese because muscle weighs more than fat. Athletes, bodybuilders, and highly active people should consider additional measures like body fat percentage, waist circumference, or body composition analysis.
How does BMI calculation differ for children and teenagers?
BMI calculations for children and teens account for age and gender differences in growth patterns. Pediatric BMI is expressed as a percentile relative to others of the same age and sex, rather than using the standard categories for adults.
Can BMI be inaccurate for Asian populations?
Research shows that Asian populations may have higher health risks at lower BMI levels compared to Caucasians. Some health organizations recommend different BMI cutoff points for Asian individuals to account for these differences.